The knowledge of service rules is very important in badminton to not be called for faulty services. An illegal service not only costs vital points but also the lapse of concentration is not good for the health of your gameplay. At the early stage, you should be aware of the badminton service rules to make it a habit in the subsequent stages to deliver proper service following all the rules and regulations as guided by the BWF (Badminton World Federation).
My previous article, “Badminton Rules for Singles and Doubles Game” is about the generalized ideas on every type of rule whereas this article only concentrates on the serving rules.
General Rules of Serving in Badminton for Singles and Doubles
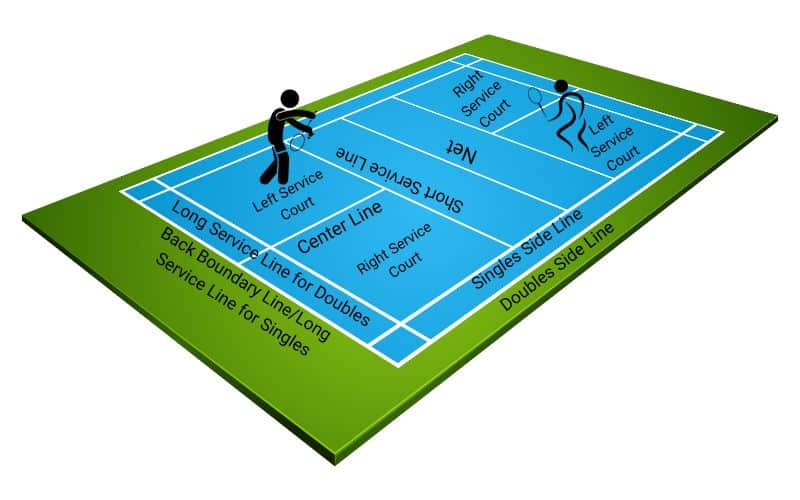
The following are the general service rules that are applicable for both singles and doubles.
The server and receiver must stand within their respective service courts (which are diagonally opposite) without touching any of the lines.
At the time of delivering service, some parts of both feet of the server and receiver must be in touch with the ground until the shuttlecock is hit.


The shuttle should be below the server’s waist height at the time of serving. This common practice is being widely followed in recreational and club-level tournaments.
But in 2018, BWF introduced a new fixed height system in the badminton service rules, which has been followed in international tournaments.
“The whole of the shuttle shall be below 1.10 meters from the surface of the court at the instant of being hit by the server racket.”
The racket head and the shaft must be pointed downwards at the instant of delivering the service.
After taking the initial backswing, the movement of the racket should be a continuous and forwarding motion.
While serving, your racket must strike the base of the shuttle, i.e. the cork. You are not allowed to hit feathers and take advantage of the huge amount of spins during service.
You are not allowed to move while delivering service
After hitting, the flight of the shuttlecock should take an upward trajectory aiming towards the diagonally opposite half of the service court.
If you miss the shuttle, the service is considered to be delivered.
A service should not be attempted until the receiver is ready. Once the server and receiver are ready, there should not be any delay in the execution of the service.
What are the Badminton Service Court Rules in Singles?
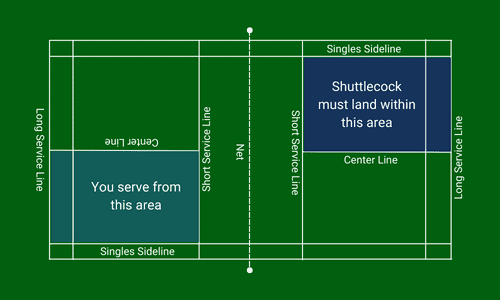
The area bounded by the short service line, long service line, center line, and the singles sideline, is the service court in singles.
There are two service courts in each half, i.e.the right service court and the left service court. To be a valid service, the shuttlecock must land within the receiver’s service court if not intercepted by the receiver.
Any service short of the short service line or beyond the long service line is considered wrong. Likewise, if the shuttlecock lands outside the centerline or the singles sideline, it is also a wrong service.
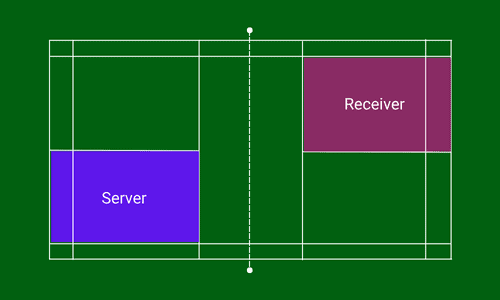
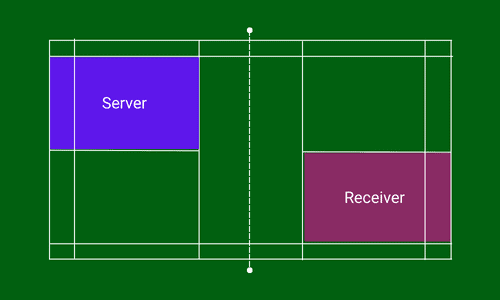
The service will be taken from the right service court if the score of the serving player is an even number (0, 2, 4, …). The receiver stands on the diagonally opposite service court to the server.
It is just the reverse when the score of the server is an odd number (1, 3, 5, …). He will serve from the left service court to the receiver standing diagonally opposite service court i.e. his/ her left service court.
What are the Badminton Service Court Rules in Doubles?

The service court in doubles is different than in singles. Four lines take into account the doubles service court, i.e. short service line, long service line, centerline, and the doubles sideline. The area bounded by these 4 lines, represents the doubles service court.
Lengthwise a doubles service court is shorter than a singles service court. So for doubles, you should take care of high services that may go beyond the long service line but may be well in for singles.
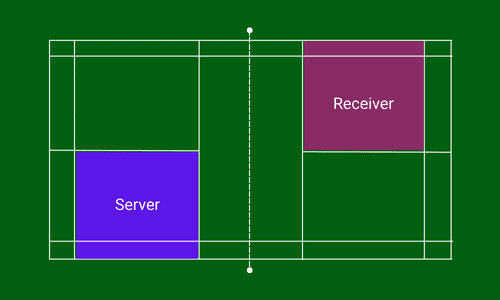
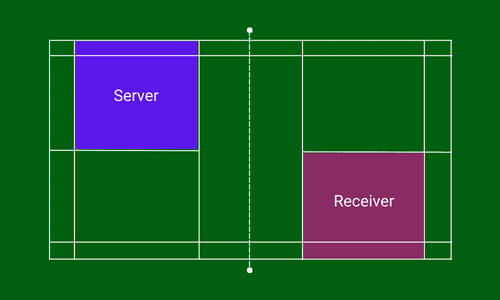
The same rules of singles also apply in doubles, i.e. for even points (0, 2, 4, and so on), you have to serve from the right service court, and for odd points (1, 3, 5, …), it is the left service court. But for doubles, the switching of service courts looks a bit confusing. So I have presented it with the help of examples and pictures to make it more convenient for you.
Suppose two teams, X and Y take part in a doubles match. Team X consists of players A and B whereas Team Y consists of C and D.
Only players of the serving team who win the point, exchange their respective service courts. If the point is won by the receiving team, all players of both teams remain in the same service courts.
Sequence 1
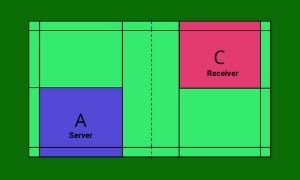
Player A of team X serves first from the right service court (as the score is an even number, i.e. 0-0). Player C is on the right service court, which is diagonally opposite of player A.
Sequence 2
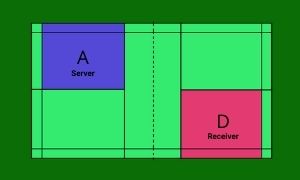
Team X wins the point. So player A takes the opportunity to serve from the left court (as the score is an odd number, i.e. 1-0) to D, player of the opposite team Y, standing on the left service court.
Sequence 3
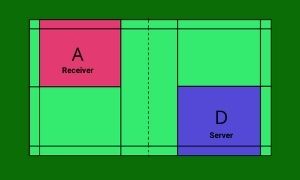
The receiving team, Y wins the next point. So all players remain in the same courts and D serves from the left service court ( Score is 1-1, an odd number) to player A of team X.
Sequence 4
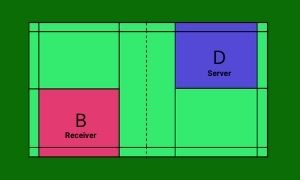
Team Y wins the point. So the players of team Y exchange their positions and D serves from the right service court (Score is 1-2, an even number) to player B standing on the diagonally opposite service court.
Sequence 5
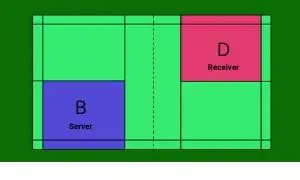
The receiving team, X wins the next point. So B is the new server and serves from the right service court (Score even number, i.e. 2-2) to D of team Y.
The sequence of serving and receiving will continue in this pattern till the match ends.
What are the Service Court Errors?
- If a server/ receiver serves or receives out of his turn
- If the server/ receiver is in the wrong service court while delivering/ receiving the service.
If a service court error is identified after the delivery of the next service, it is not to be corrected. But if it is discovered before the delivery of the next service, the following actions shall be taken.
- If the faulty side (server or receiver) wins the rally, the service is replayed with corrected positions.
- In case the error is made by both sides, the service is retaken with corrections.
- If the faulty side loses the rally, the error will not be corrected and play will continue with the same score without changing the corrected service courts.
What is ‘let’ in Service?
A let serve occurs when the service is interrupted and replayed with the existing points. There are some situations when a service is called let.
- If the service is delivered before the receiver is ready
- If some feathers get separated from the base
- If both server and receiver are on the wrong service court
- If the winner of a rally (server or receiver) is on the wrong service court
- If the shuttlecock passes the net but gets stuck on the top of the net
Who serves first in badminton?
In the opening set, the winner of the toss has the opportunity to serve first. For the 2nd and 3rd sets, the winner of the previous set serves 1st in the following set. This follows the badminton service rules. The simplicity is that when you win a set, you also have won the last point. So you will start serving the next set because you are the winner of the last point.
What happens if the shuttlecock clips the net but drops inside the service box?
This type of occurrence generally happens during the low serve in badminton when you have to be precise on the shuttle trajectory. In this case, there is no deviation from the general serving rules. If the shuttlecock falls short of the short service line, your opponent wins the point, otherwise, it is perfectly right when the shuttlecock is inside the service court.
Can you move during a service?
No player (server or receiver) is allowed to move his feet off the ground before the shuttlecock is struck by the server. The instant the server hits the shuttlecock, both players are allowed to move their feet off the ground.
Is overhead service allowed in badminton?
The rules of badminton are not like tennis where the server hits the ball above his/ her head. In badminton, the server points the head of the racket downwards and after the initial backswing, the racket follows a continuous forwarding motion till the shuttlecock is struck.
Is it the right service if the shuttlecock lands on the line?
All lines of a service court are parts of the service area. When you hit a shuttlecock, the head of the shuttle lands first. If the head of the shuttlecock touches the lines of a service court, it is considered in.
Where does the doubles partner of the server/ receiver stand during a service?
There are clear instructions regarding the court position of the server or receiver. For an even score, the server serves from the right service court and for an odd score, the service is taken from the left service court. But there are no such rules about the positions of their partners. They may stand anywhere within the respective courts as long they don’t obstruct the vision of the receiver or server.
Related Topic:




